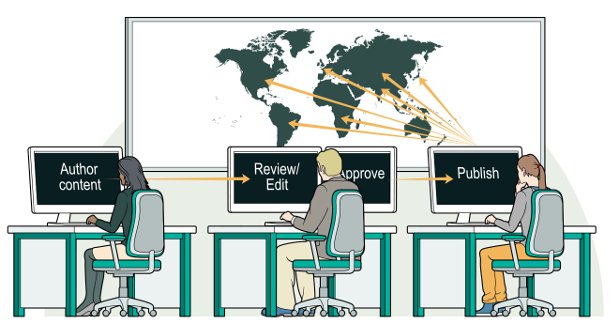
Website Localization EHSAAS RASHAN PROGRAM refers to the process of adapting a website’s content, language, design, and functionality to suit the cultural, linguistic, and technical preferences of a specific target audience in different countries or regions. It involves not only translating text but also ensuring that the entire user experience feels native to the target audience .
Website Localization
Key aspects of website localization include:
- Language Translation: Adapting all text on the website into the language(s) spoken by the target audience.
- Cultural Adaptation: Ensuring that images, symbols, colors, and other design elements are culturally appropriate and resonate with the target audience.
- Technical Adaptation: Adjusting formats, currencies, date formats, and other technical aspects to align with local conventions Globalization Partners EHSAAS RASHAN PROGRAM.
- SEO and Keywords: Optimizing content with relevant keywords and phrases for local search engines to improve discoverability.
- User Experience (UX): Ensuring that navigation, layout, and functionality meet the expectations and preferences of the local users.
- Legal and Regulatory Compliance: Adhering to local laws and regulations concerning data privacy, consumer rights, and other legal aspects.
Effective website localization enhances user engagement, improves conversion rates, and builds credibility in new markets by providing a seamless and culturally relevant experience Globalization Partners EHSAAS RASHAN PROGRAM.
 Website Localization EHSAAS RASHAN PROGRAM Services
Website Localization EHSAAS RASHAN PROGRAM Services
Website localization services also called “website translation services” are a must for companies that want to expand the markets for their products and services by publishing their website in several languages. GPI helps clients produce accurate, culturally appropriate, search engine optimized content for their multi-language websites. Whether you use standard website publishing tools and workflows or have the latest, enterprise wide web content management system, GPI works with your in-house web team or your external agency to author and publish websites in any language and for any locale.
GPI stands for Globalization Program Initiative, a framework designed to streamline and optimize the localization processes for products and services across different markets. It encompasses various aspects such as:
- Strategy Development: Creating a roadmap for global expansion and localization efforts tailored to specific markets and regions.
- Content Management: Implementing systems and processes to efficiently manage multilingual content creation, translation, and adaptation.
- Technology Integration: Utilizing tools and platforms that support translation memory, terminology management, and workflow automation to enhance efficiency and consistency.
- Quality Assurance: Implementing rigorous testing and validation processes to ensure linguistic accuracy, cultural relevance, and functional integrity across localized products.
- Market Research and Analysis: Conducting thorough research on target markets to understand cultural nuances, consumer behavior, and market trends.
- Continuous Improvement: Iteratively refining localization strategies based on feedback, performance metrics, and evolving market dynamics.
GPI aims to enable companies to effectively engage with global audiences, maximize market penetration, and maintain brand consistency while respecting local preferences and regulations.
Introduction to Website Localization
Website localization is the process of adapting a website to make it linguistically, culturally, and contextually suitable for a specific target audience in different regions or countries. It involves more than just translation; it encompasses understanding local norms, preferences, and behaviors to create a seamless user experience that resonates with the target market.
Key Elements of Website Localization
Effective website localization entails several key elements. Firstly, linguistic adaptation ensures that content is accurately translated into the local language, considering nuances, idiomatic expressions, and regional dialects. Secondly, cultural adaptation involves adjusting images, colors, symbols, and even layout to align with cultural norms and preferences. For instance, colors that symbolize different meanings in various cultures must be carefully chosen to avoid misunderstanding or offense. Thirdly, technical adaptation ensures that the website functions smoothly in terms of date formats, currencies, measurement units, and legal requirements specific to the target market. Lastly, SEO localization involves optimizing content for local search engines, using relevant keywords and meta tags that resonate with local users’ search behaviors.
Benefits of Website Localization
Website localization offers numerous benefits to businesses aiming to expand their global presence. It enhances user experience by providing content in users’ native languages, thereby increasing engagement and reducing bounce rates. Moreover, it builds trust and credibility among local users, as they perceive the website as being tailored specifically to their needs and preferences. From a marketing perspective, localized websites are more likely to attract organic traffic from local search engines, leading to higher conversion rates and improved ROI on marketing efforts. Furthermore, localization facilitates easier market entry and adaptation, allowing businesses to penetrate new markets more effectively and compete with local competitors.
Challenges in Website Localization
Despite its benefits, website localization presents several challenges that businesses must address to ensure success. One major challenge is maintaining consistency across different language versions while adapting content to reflect cultural nuances. This requires careful coordination between translators, content creators, and localization specialists to ensure unified brand messaging. Another challenge is managing updates and changes across multiple localized websites, as each version may require separate maintenance and testing. Additionally, ensuring technical compatibility and performance across different devices and internet speeds in target markets can be complex and resource-intensive. Moreover, the cost of localization, including translation, cultural adaptation, and technical adjustments, can be significant, particularly for small and medium-sized enterprises with limited budgets.
Best Practices for Effective Website Localization
To overcome these challenges and achieve successful website localization, businesses should adopt several best practices. Firstly, conducting thorough market research to understand local preferences, consumer behavior, and competitors’ strategies is crucial. This informs content creation and design decisions that resonate with the target audience. Secondly, collaborating with experienced localization professionals who understand both linguistic and cultural nuances ensures high-quality translations and cultural adaptation. Utilizing translation management systems and content management systems that support multilingual websites can streamline the localization process and facilitate content updates across different language versions. Moreover, conducting usability testing and gathering feedback from local users help identify and address usability issues or cultural misunderstandings early in the localization process. Lastly, continuously monitoring website performance and making iterative improvements based on analytics and user feedback ensures ongoing relevance and effectiveness of localized websites.
Conclusion
In conclusion, website localization is a strategic imperative for businesses seeking to expand their global footprint and effectively engage with diverse international audiences. By adapting content, design, and functionality to align with local languages, cultures, and preferences, businesses can enhance user experience, build trust, and drive growth in new markets. While website localization presents challenges such as maintaining consistency, managing costs, and ensuring technical compatibility.